How Does Age Affect Diabetes?
According to WebMD, one of the biggest risk factors for developing diabetes is age.
In fact, a person’s risk of developing Type 2 diabetes increases dramatically after the age of 45. How do aging and diabetes affect each other? And what complications of diabetes increase as we age? Read and learn more about this to have a better understanding and protect your health!
📌 How does age affect diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive chronic condition. In fact, did you know that you can have diabetes for 5 – 10 years and not even know it? The prevalence of diabetes dramatically increases after 45 years of age.
- Decrease in the amount of insulin secreted
- Increase in insulin resistance caused by:
– A change in body composition where there is an increased amount of fat stored deep inside the belly, wrapped around the organs
– Loss of muscle mass - Reduced physical activity
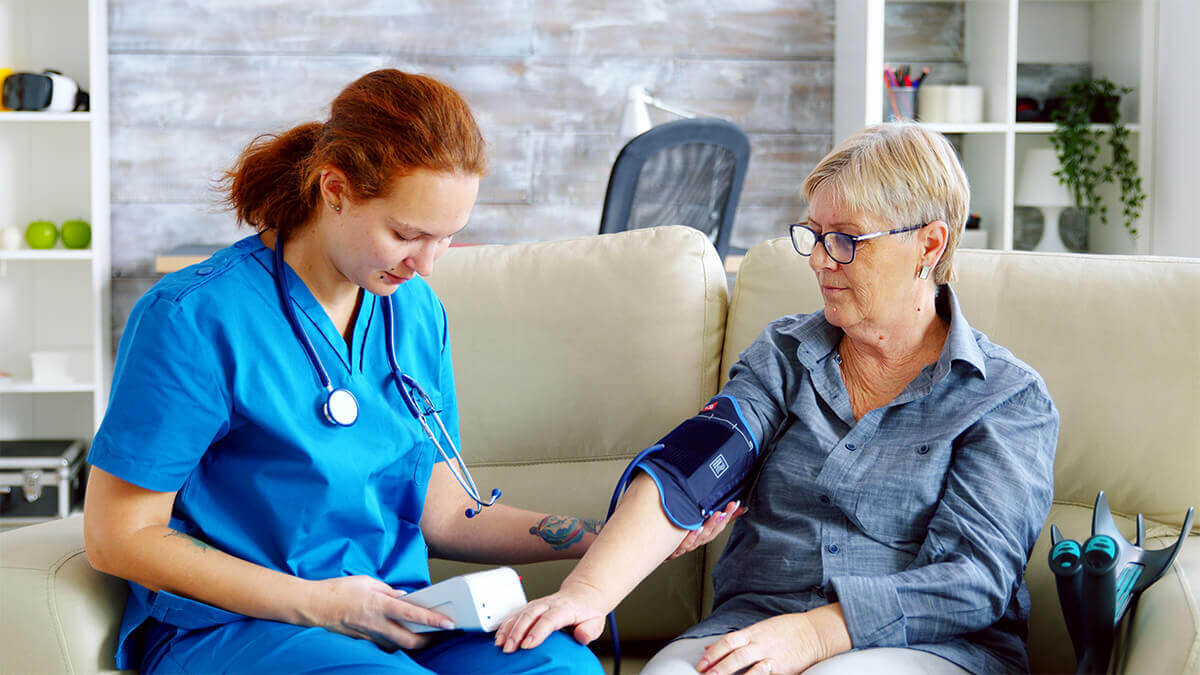
📌 What complications of diabetes increase with age?
According to the Endocrine Society, 33% of adults aged 65 or older have diabetes. This population is more at risk of developing diabetes-related complications like high blood pressure, heart disease, kidney failure, and obesity than younger people living with diabetes.
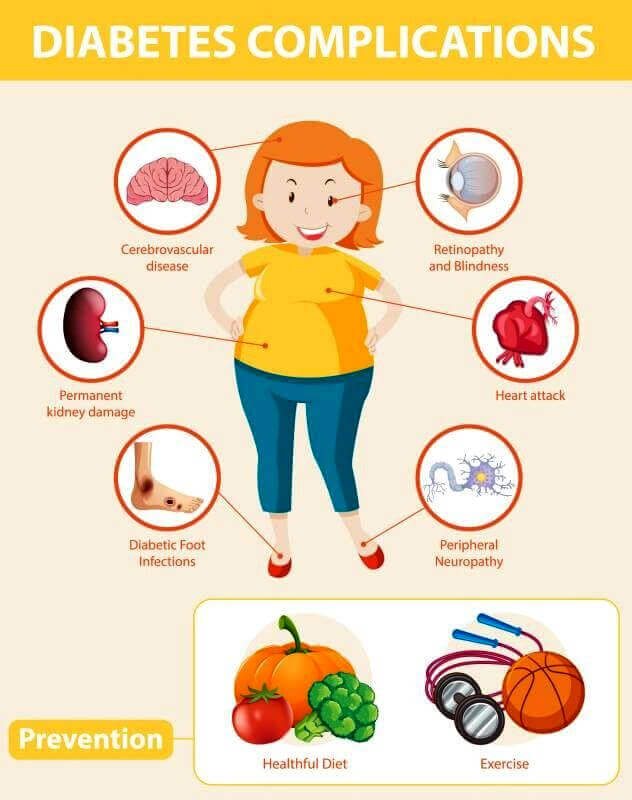
📌Prevention
Special considerations should be addressed to support overall health and quality of life especially when you get older. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends that all adults who are 45 years or older should be screened for diabetes in the clinical setting every 1-3 years. If you are interested in a wellness screen at Iowa Diabetes, you are in luck. We offer free wellness screenings that include an A1c and a blood sugar check.
The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) has shown that interventions in lifestyle like changing to a healthy eating pattern and increasing physical activity are very effective in those over the age of 60 years with diabetes. Check out some of our other blogs and videos on tips and tricks for making these changes.
Summary The risk of Type 2 diabetes does increase as we age, but knowing your risk as soon as possible can help you take the right steps to manage it or even prevent it. If you are over the age of 45, getting screened is probably one of the most important steps that you can take to understand your risk.
Disclaimer: Any information provided is not intended as medical advice. Iowa Diabetes is not responsible for any information from third parties.