
Say Goodbye to Post-Meal Sugar Spikes: Try These 5 Fixes
Take control of your post-meal blood sugars with these five steps to make a positive difference in your daily diabetes management.
? Meal Time Insulin
The timing of your mealtime insulin is very important for managing post-meal blood sugar spikes. Taking insulin too late after eating can lead to a rapid increase in blood sugar. On the other hand, if you take your insulin too early, it increases the risk of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) during your meal. There are two main types of mealtime insulin: Fast-acting and ultra-fast-acting, each with its ideal administration times.
- Fast-Acting Insulin: Administered up to 15 minutes before a meal. This gives the insulin enough time to start working by the time carbohydrates begin to raise your blood sugar.
- Novolog (insulin aspart)
- Humalog (insulin lispro)
- Apidra (insulin glulisine)
- Ultra-Fast-Acting: These insulins have a quicker onset of action and can be given right at mealtime.
- Fiasp (insulin aspart)
- Lyumjev (insulin lispro-aabc)
⚖️Carb Insulin Ratios
Carbohydrate ratios are important for anyone who doses insulin based on the amount of carbs they eat. This ratio tells them how many grams of carbohydrates will be covered by 1 unit of insulin. For example, if your insulin-to-carb ratio is 1:15, this means you will need 1 unit of insulin for roughly every 15 grams of carbohydrates you consume.
To correctly determine how many units are needed, you need to know how many carbs are in your meal or snack. The best way to figure this out is by reading the nutrition label, where you will find listed the total carbohydrate amount that you are eating. It is important to look at the serving size when calculating carb amounts. Two servings mean that you need to double the number of carbs listed on the nutrition label.
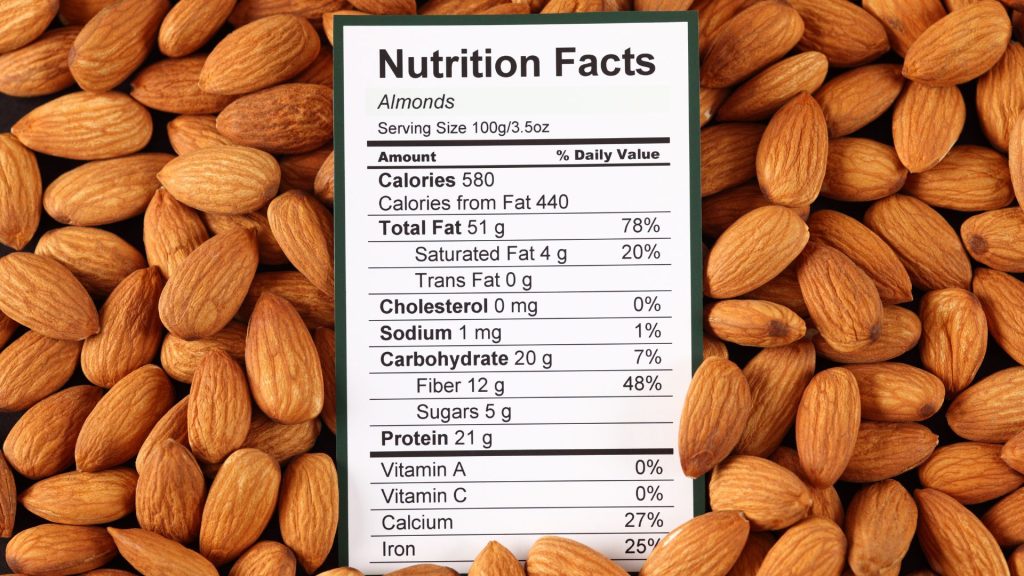
? Food Consumption
Iowa Diabetes offers some great resources that can be a perfect fit for your diabetes goals in the new year.
Thinking about what and how you eat plays a critical role in managing post-meal sugar levels. Eating too many carbohydrates at once can lead to spikes in your blood sugar. One strategy to prevent this is to pick foods that are lower in carbohydrates and to eat protein before your carbs. Protein helps slow digestion and control rises in blood sugars.
?Testing Blood Sugars
Keeping an eye on your sugars is one of the best things that you can do to manage your diabetes. A continuous glucose monitor can make this process easier by giving you real-time data and trends throughout the day. If you do not have a CGM, you can still effectively check your blood sugar manually using a traditional meter and finger prick.
Timing your blood sugar checks should be done properly. Don’t test your blood sugars directly after eating your meal, as your body has not had time to digest and absorb the carbohydrates. Instead, check your blood sugars around 30 minutes to an hour post-meal to get a better estimate of how your food affects your glucose. According to the American Diabetes Association, a good goal is to keep your two-hour post-meal blood sugars below 180 mg/dL. Regularly monitoring your blood sugar helps you to identify patterns and learn how different foods impact your blood sugar, allowing you to make better food choices.
??♂️➡️ Staying Fit
Staying active is one of the most effective ways to support a healthy blood sugar level. Your goal should be to aim for at least 150 minutes of exercise a week adding in 2-3 days per week of resistance exercise. Physical activity helps to reduce insulin resistance, meaning your body can use insulin more effectively to manage glucose levels. If you notice a trend of high blood sugars after meals, you could try adding a short 15-20 minute walk after dinner. This short walk can help to lower your post-meal glucose and give you more controlled overall sugar levels.
Summary
There are multiple things that you can do to help prevent post-meal blood sugar spikes. The key is finding what works best for YOU. Whether it’s improving your carb counting, timing your insulin more effectively, adjusting your meals, or implementing more regular activity, each of these tools can play a role in maintaining steady blood sugar levels after eating.







I just can’t seem to get my A1C down. I would appreciate the assistance.
Hi Brenda, thank you for reaching out. Kindly call us at 515-329-6800 and our team can guide you on the various diabetes care options we offer and the ones that would work best for your health.